What is Damp?
Structural damp is the presence of excess moisture in the walls, floors or ceilings of a building.
There are three main types of damp:
Rising Damp
Penetrating Damp
Condensation
What is
Rising Damp?
Rising damp is caused by water rising from the ground into the walls of a building through capillary suction of brick or stone. Water breaks through or around a broken damp proof course (DPC) and rises into the wall through the porous mortar and masonry used.
This type of damp only affects ground floor rooms and basements. Rising damp will usually rise up a wall to almost 1 metre, after which the shear weight of the water and the effect of gravity prevents it rising further – only with exceptionally thick brickwork could the damp rise to a maximum of 1.2 metres. Rising damp usually leaves a tide mark on the wall, you may also notice salt crystals on the affected areas of the interior part of the external walls which often looks like a white or off-white powder on the wall, paint may also be flaking as a reaction to those salts.
What Does Rising Damp look like?

What is
Condensation?
Condensation occurs on surfaces that are colder than the dew point (the dew point is the temperature a surface needs to be in order have water droplets appear) . The dew point depends on the humidity levels in the air. When the relative humidity level in the air is high, the dew point will also be high, therefore it is important that the humidity levels in the air are reduced to a minimum by ventilating.
When there is a lack of ventilation and humidity levels remain high in the property, mould is able to grow. Mould typically grows on damp surfaces that have become damp due to high humidity levels in the property.
Because windows and corners tend to be the coolest areas in a house, condensation is often found on or near those areas. In order to prevent condensation issues, it’s important to keep a dry home, ensuring circulation of damp air caused by cooking, showering, drying clothes, etc.
What does condensation look like?

What is
Mould?
Mould is a fungus that requires high levels of moisture to survive. Mould spores exist in the atmosphere and are invisible to the human eye. They only become visible when they rest on a surface, where they can grow and multiply if untreated. Depending on the type of mould, the appearance varies. Black mould is very common in homes that have high levels of condensation. For mould to be able to germinate on a surface, it requires the surface to be wet with condensation.
What to do if you have mould in your house
If you see the early stages of mould, it’s important to clean it off the surface with a bleach or fungicidal wash. Be careful not to upset mould by brushing, dusting or vacuuming. This can cause the mould to spread to other areas of the house.
If soft furnishings or carpets have been affected by mould, it’s important to clean them thoroughly to remove the mould spores. Carpets will need to be shampooed and soft furnishings dry cleaned.
What does mould look like?

How to get rid of damp
Getting rid of damp involves three key actions:
- Locate the source of the excessive moisture
- Remove mould that has built up inside the property
- Take action to control moisture and condensation
In order to locate the source of moisture, it’s important to understand where it may be building up.
You should check for leaking pipes and build up around water overflows.
If your home is a new build, the walls could show signs of damp as the plaster is still drying out. If this is the case, it’s important to heat and ventilate your home. Using a dehumidifier will also help speed up this process.
If the damp appears on the ground floor, the issue could be due to rising damp. You can read more about that here.
If the source of moisture doesn’t appear to be caused by structural faults in the building, the build up is probably due to condensation.
What is a damp course
The damp proof course acts as a barrier and prevents this rise of water from the ground into the walls. It is a horizontal layer of waterproof membrane that is built into the structural walls of a building just above ground level. For older properties that were built before 1920, a damp course may not have been laid and water may be passing through the natural brickwork or other material used under the floor at ground level.
What to do when a house is damp
To eradicate damp from your property, it’s essential that you treat the cause of the problem. With a range of damp proofing solutions on the market, it’s worth doing your research to see which solution is most suitable for your property.The solution to rising damp caused by a moisture bridge in a cavity will be different to the solution for damp that is caused by rising water levels in the ground. Quick fixes like repointing brickwork or painting rarely work and only serve to superficially cover up the problem while it deteriorates out of sight.
What does damp cost to fix?
The cost of damp treatment will depend on the extent of water ingress and the type of building materials that have been affected. If remedial works significantly affect your home’s structure, then traditional damp treatment and reconstruction work can easily run into thousands of pounds.
Traditional damp proofing methods almost always require some exterior work and plastering in the interior of your home. Obviously, you can save a considerable amount if you’re capable of carrying out this kind of interior work yourself. However, if you’re not experienced it’s worth seeking the advice of a professional before undertaking work as it can end up being more costly in the long term if it eventually has to be replaced.
If your damp proof course has been damaged, it will have to be fixed by an experienced tradesman. The damp proof runs under the entire floor and the ground floor walls of your property, which complicates things when it comes to finding the exact spot where it has ruptured. For this reason, the most common remedial method is to inject a chemical treatment to prevent further issues.
Silicone injection repairs costs vary from a few hundred pounds for a single wall of a terraced house to up to ten thousand pounds for an entire detached property, prices may vary significantly between different companies. In the case that asphalt tanking needs to be installed in your property, these prices go up.
Bear in mind that damp proofing chemicals are very strong. Precaution needs to be taken when handling these and they should really only be used by trained professionals. Not only can they burn your skin, but they can also cause respiratory problems if inhaled. It is important to steer well clear of these chemicals when they are drying out and always keep children and pets away from the areas that have recently been treated.
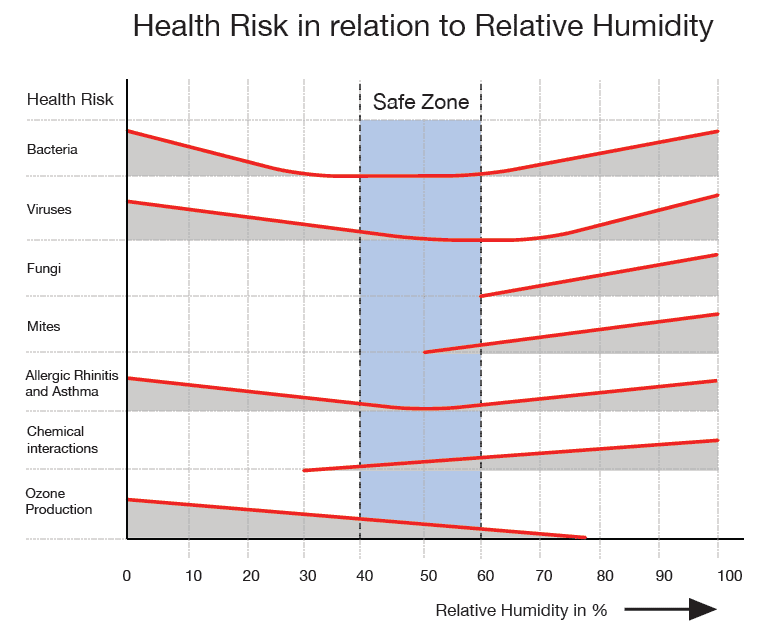
Health risks in relation to relative humidity
A stable relative humidity of around 50% in the home is crucial to maintaining a healthy living environment. Damp problems have a direct impact on your respiratory health and if the issue goes untreated, creates a significant risk.
If the relative humidity of your home or workplace is constantly too high, it will affect your health in the form of:
Maximum infection by bacteria 0-30%, and 60-100%
between maximum infection by 0-50%, and 70-100%
viruses between fungi grow from 60% – 100%
dust mites grow from chemical 50% – 100%
reactions increase dramatically 50% – 100%
Diseases caused by air transmissible infectious bacteria and viruses are minimised by exposure to relative humidity between 40 – 70%. In addition, the size of the allergic mite population and the amount of fungi is directly dependent on the relative humidity.
At a rate of 80%, which is quite common for homes in Britain, dust mite population reaches peak growth.
Most fungi grows at rates of 60% or more. Besides that, chemical substances like nitrogen dioxide, formaldehyde, sulfur and ozone can be released from building materials as a result of excessively high or low Rh levels.
How to stop damp
We offer solutions that are proven to remove damp associated with each of the three main causes of damp.
Treat condensation, rising and penetrating damp for good.
Allow the walls of your home to breathe.
Ensure a clean and healthy living environment.
Plan a free damp assessment.
Feel free to contact us for a free damp survey or advice from our damp expert.


